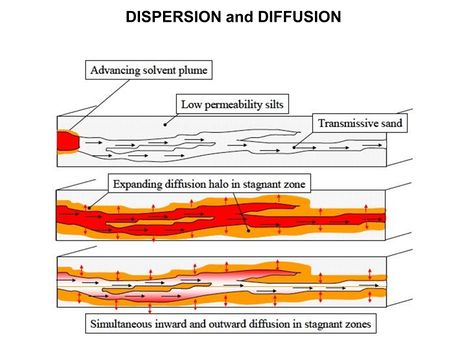
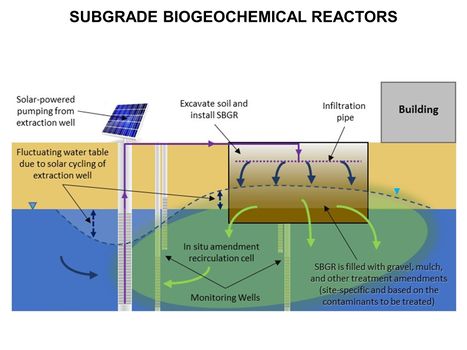
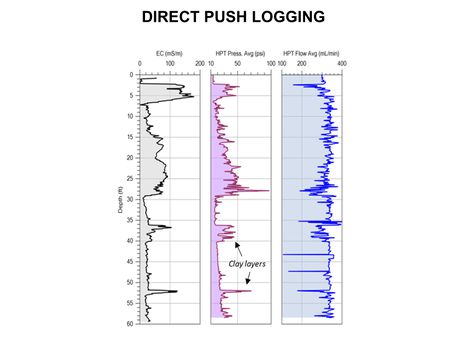
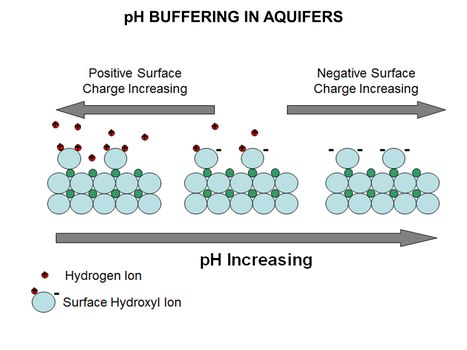
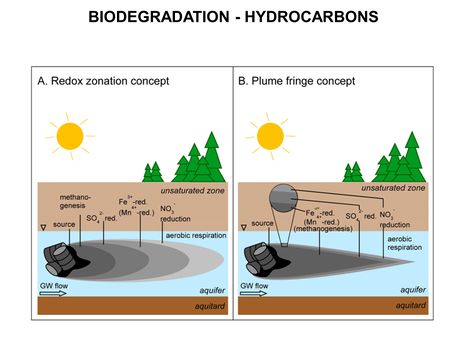
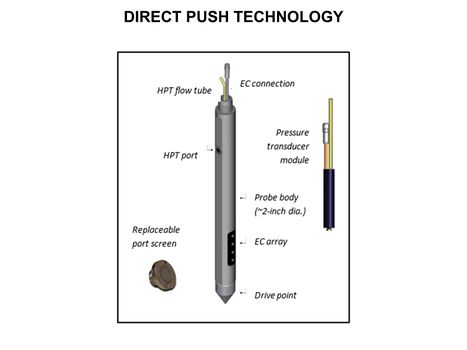
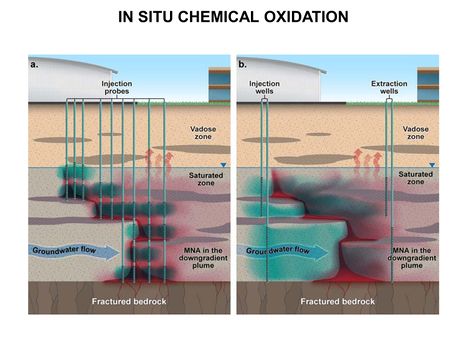
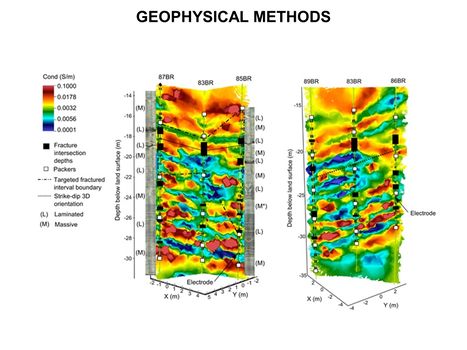
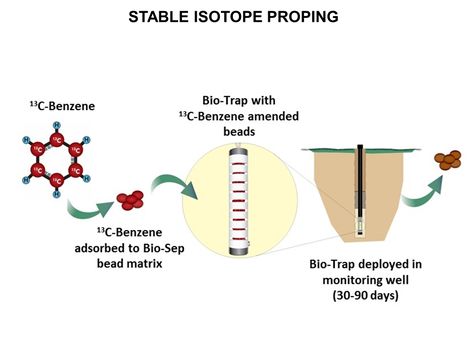
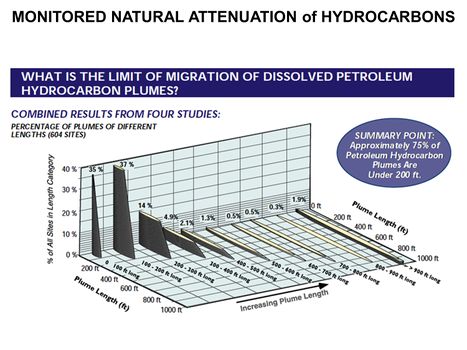
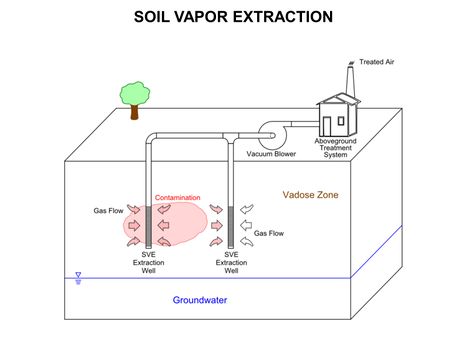
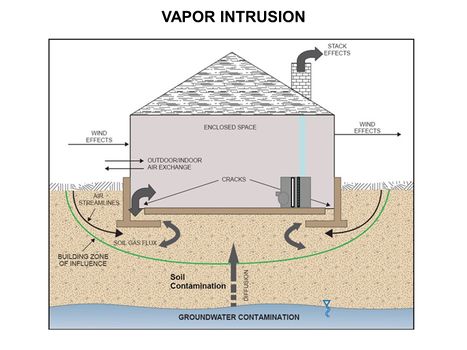
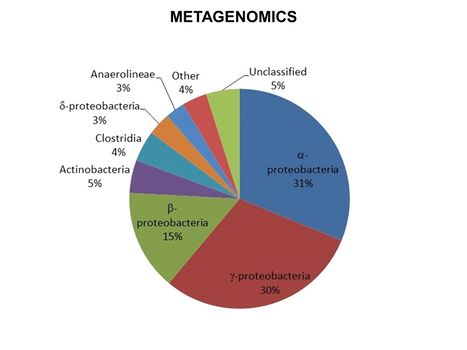
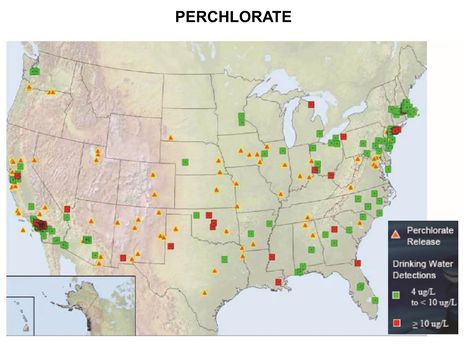
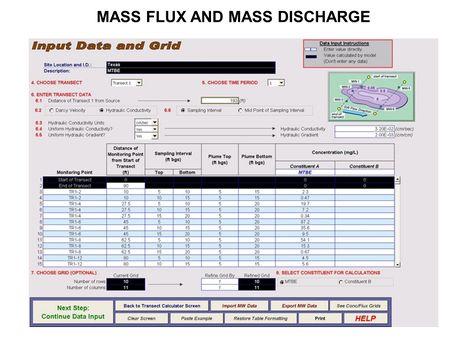
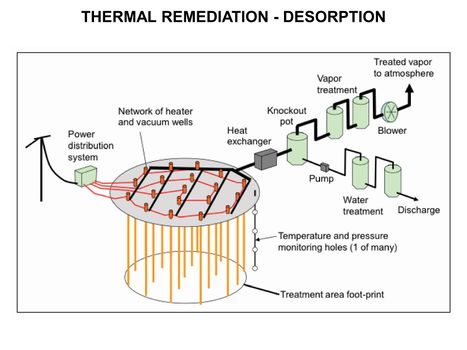
Main Page
Peer Reviewed. Accessible. Written By Experts |
Your Environmental Information Gateway |
| The goal of ENVIRO Wiki is to make scientific and engineering research results more accessible to environmental professionals, facilitating the permitting, design and implementation of environmental projects. Articles are written and edited by invited experts (see Contributors) to summarize current knowledge for the target audience on an array of topics, with cross-linked references to reports and technical literature. | See Table of Contents |
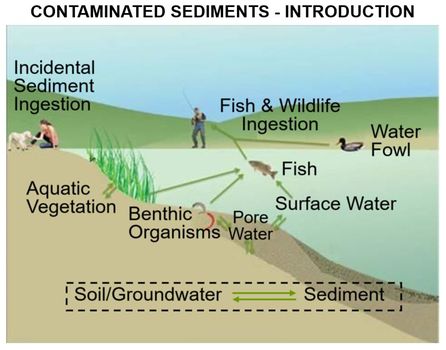
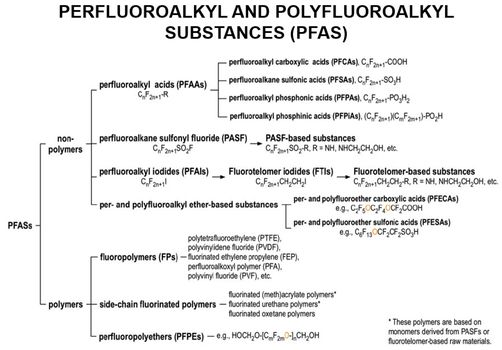
Featured article: PFAS Monitored Retention (PMR) and PFAS Enhanced Retention (PER)Groundwater sites contaminated with PFAS are difficult to investigate and remediate due to strict cleanup goals, lack of natural degradation mechanisms for some PFAS, and the high mobility and persistence of several PFAS. As a result, understanding and potentially relying on processes that reduce PFAS migration rates and mass discharge rates is of considerable interest to site managers. This includes a variety of chemical and geochemical retention processes that have been incorporated into the PFAS Monitored Retention (PMR) approach. PMR is a similar concept to monitored natural attenuation (MNA), and the term has recently been adopted in place of MNA to avoid potential confusion with destructive and/or permanent attenuation processes that are part of the MNA strategies for other constituents of concern (COCs). However, many of the processes remain the same, and they are expected to reduce PFAS concentrations and mass discharge during transport from source areas. A key concept of PMR is that retention processes can provide a credible scientific basis for attenuation of PFAS concentrations or mass discharge over time (or distance) that reduce the mobility and risk associated with PFAS in the subsurface. PMR may have applicability as a sole remedy at low-risk sites, but it could also help control low levels of remaining contamination after active treatment. It may also serve as a temporary remedy at sites with no proximate receptors, giving time for the development of more cost-effective technologies. Finally, it can be part of a treatment train at more complex sites where risk-based approaches are acceptable.
(Full article...)
|
Enviro Wiki Highlights |