Difference between revisions of "Main Page"
TLieberman (talk | contribs) |
m |
||
| (495 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | < | + | <center> |
| − | + | {| class="MainPageBG" style="margin: auto; width: 95%; border-spacing:0px;" | |
| − | {| | + | |- |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width:55%;" |<center><span style="font-size:175%; line-height: 0.2em; vertical-align:top;"><big><span style="color:#008566">Welcome to '''ENVIRO'''</span> <span style="color:#762a87">'''Wiki'''</span></big></span><br /><br /><br /><span style="font-size:150%; color:#008566; line-height: 0.2em; vertical-align:top;"> Peer Reviewed. Accessible. Written By Experts</span></center> |
| − | < | + | | style="width:40%;" |<center><span style="font-size:110%; vertical-align:top;"> ''Developed and brought to you by '' <br>[[File:MainLogo-serdp-estcp.png|link=https://www.serdp-estcp.org |frameless|center|350px]]</span>''<span style="font-size:140%; vertical-align:top;">Your Environmental Information Gateway</span>'' |
| − | + | </center> | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | < | + | |<span style="width:55%; line-height: 0.3em;"> The goal of ENVIRO Wiki is to make scientific and engineering research results more accessible to environmental professionals, facilitating the permitting, design and implementation of environmental projects. Articles are written and edited by invited experts (see [[Contributors]]) to summarize current knowledge for the target audience on an array of topics, with cross-linked references to reports and technical literature. </span> |
| − | < | + | |<center><span style="font-size:130%"><br />[[#Table of Contents|See Table of Contents]]</span> |
| − | < | + | </center> |
| + | <inputbox> type=fulltext | ||
| + | placeholder=Search Enviro Wiki | ||
| + | break=no </inputbox> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | <!-- | + | </center> |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | {| role="presentation" id="mp-upper" style="margin: auto; width: 95%; margin-top:3px; border-spacing: 0px; " | |
| − | + | <!-- TODAY'S FEATURED ARTICLE --> | |
| − | + | | id="mp-left" class="MainPageBG" style="width:55%; padding:0; vertical-align:top; color:#000;" | | |
| − | + | <h2 id="mp-tfa-h2" style="margin:0.5em; background:#cef2e0; font-family:inherit; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> Featured article: Restoration of Ecological Function in Terrestrial Systems Impacted by Invasive Species</h2> | |
| − | | | + | <div id="mp-tfa" style="padding:0.0em 1.0em;">[[File:ThierryFig1.png|450px|left|link=Restoration of Ecological Function in Terrestrial Systems Impacted by Invasive Species]]<dailyfeaturedpage></dailyfeaturedpage> |
| − | + | [[Restoration of Ecological Function in Terrestrial Systems Impacted by Invasive Species|(Full article...)]] </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | | style="border:1px solid transparent;" | | |
| − | + | ||
| + | <!-- Enviro WIKI Highlight --> | ||
| + | | id="mp-right" class="MainPageBG" style="width:40%; padding:0; horizontal-align:center; vertical-align:top;" | | ||
| + | <h2 id="mp-itn-h2" style="margin:0.5em; background:#cedff2; font-family:inherit; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3b0bf; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;">Enviro Wiki Highlights</h2> | ||
| + | <div id="mp-itn" style="padding:0.0em 0.5em;"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <slideshow sequence="random" transition="fade" refresh="7500"> | ||
| + | |||
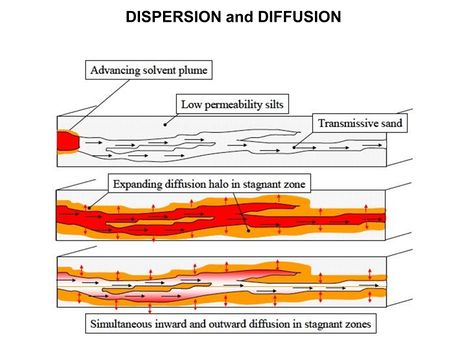
| + | [[File:WH Picture1.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Matrix Diffusion|Molecular diffusion slowly transports solutes into clay-rich, lower permeability zones]] | ||
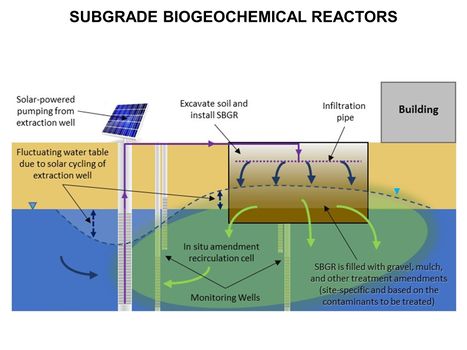
| + | [[File:WH Picture2.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Subgrade Biogeochemical Reactor (SBGR)|Typical subgrade biogeochemical reactor (SBGR) layout. The SBGR is an in situ remediation technology for treatment of contaminated source areas and groundwater plume hot spots<br/>]] | ||
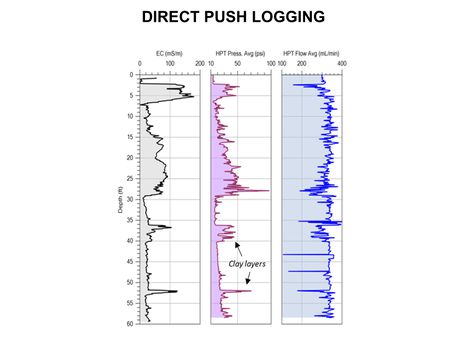
| + | [[File:WH Picture3.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Direct Push Logging|An Hydraulic Profiling Tool (HPT) log with electrical conductivity (EC) on left, injection pressure in middle, and flow rate on the right]] | ||
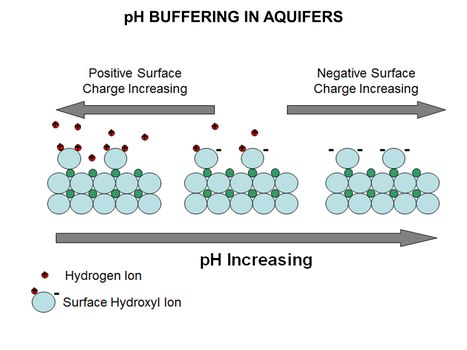
| + | [[File:WH Picture4.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=PH Buffering in Aquifers|Diagram of mineral surface exchanging hydrogen ions with varying pH. The surface of most aquifer minerals carries an electrical charge that varies with pH]] | ||
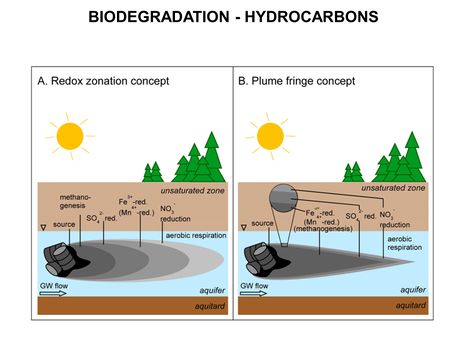
| + | [[File:WH Picture5.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Biodegradation - Hydrocarbons|Comparison of the longitudinal redox zonation concept (A) and the plume fringe concept (B). Both concepts describe the spatial distribution of electron acceptors and respiration processes in a hydrocarbon contaminant plume]] | ||
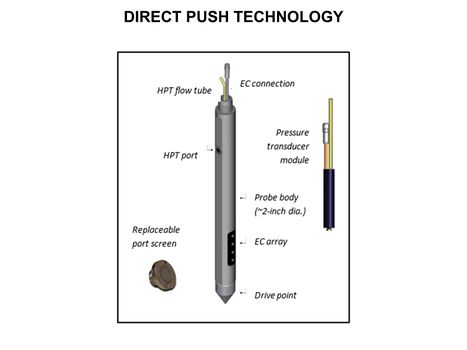
| + | [[File:WH Picture6.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Direct Push Logging|Schematic of an Hydraulic Profiling Tool (HPT) probe. HPT were developed to better understand formation permeability and the distribution of permeable and low permeability zones in unconsolidated formations]] | ||
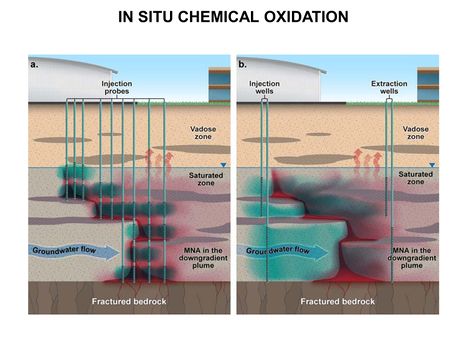
| + | [[File:WH Picture7.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Chemical Oxidation Design Considerations(In Situ - ISCO)|In situ chemical oxidation using (a) direct-push injection probes or (b) well-to-well flushing to delivery oxidants (shown in blue) into a target treatment zone of groundwater contaminated by dense nonaqueous phase liquid compounds (shown in red)]] | ||
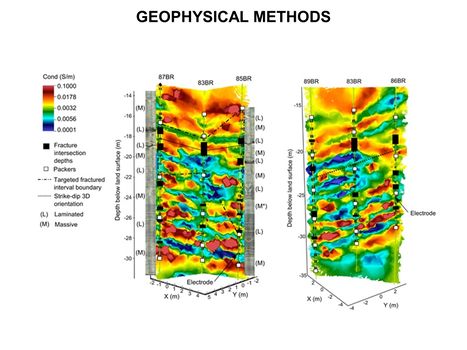
| + | [[File:WH Picture8.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Geophysical Methods - Case_Studies|High-resolution 3D cross-borehole electrical imaging of contaminated fractured rock at the former Naval Air Warfare Center in New Jersey. Cross-borehole resistivity tomography imaging is a geophysical technique that can be used for site characterization and monitoring by observing variations in the electrical properties of subsurface materials]] | ||
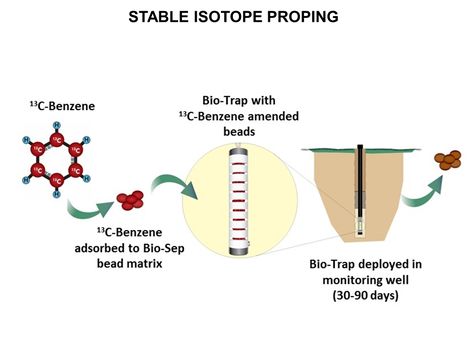
| + | [[File:WH Picture9.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Stable_Isotope_Probing_(SIP)|Stable isotope probing (SIP) in use: Loading, deployment and recovery of Bio-Trap® passive sampler with 13C-labeled benzene. Stable isotope probing (SIP) is used to conclusively determine whether in situ biodegradation of a contaminant is occurring]] | ||
| + | [[File:WH Picture10.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=1,2,3-Trichloropropane|Summary of anticipated, primary reaction pathways for degradation of 1,2,3-Trichloropropane (TCP). TCP is a man-made chemical that was used in the past primarily as a solvent and extractive agent, a paint and varnish remover, and as a cleaning and degreasing agent]] | ||
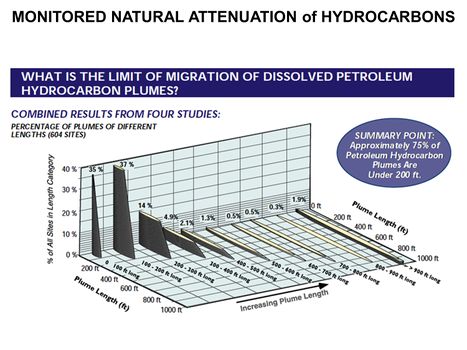
| + | [[File:WH Picture11.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Monitored Natural Attenuation (MNA) of Fuels|Distribution of BTEX plume lengths from 604 hydrocarbon sites. Monitored Natural Attenuation (MNA) is one of the most commonly used remediation approaches for groundwater contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons (PHCs) and certain fuel additives such as fuel oxygenates or lead scavengers]] | ||
| + | [[File:WH Picture12.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Groundwater Sampling - No-Purge/Passive|No-purge and passive sampling methods eliminate the pre-purging step for groundwater sample collection and represent alternatives to conventional sampling methods that rely on low-flow purging of a well prior to collection. The Snap SamplerTM is an example of a passive grab sampler]] | ||
| + | [[File:WH Picture13.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Natural Source Zone Depletion (NSZD)|Conceptualization of Vapor Transport-related Natural Source Zone Depletion (NSZD) processes at a Petroleum Release Site]] | ||
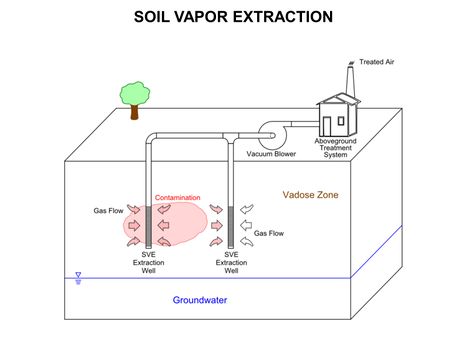
| + | [[File:WH Picture14.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Soil Vapor Extraction (SVE)|Conceptual diagram of basic Soil Vapor Extraction (SVE) system for vadose zone remediation. (SVE) is a common and typically effective physical treatment process for remediation of volatile contaminants in vadose zone (unsaturated) soils]] | ||
| + | [[File:WH Picture15.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Emulsified Vegetable Oil (EVO) for Anaerobic Bioremediation|Emulsified Vegetable Oil (EVO) mixed in field during early pilot test. EVO is commonly added as a slowly fermentable substrate to stimulate the in situ anaerobic bioremediation of chlorinated solvents, explosives, perchlorate, chromate, and other contaminants]] | ||
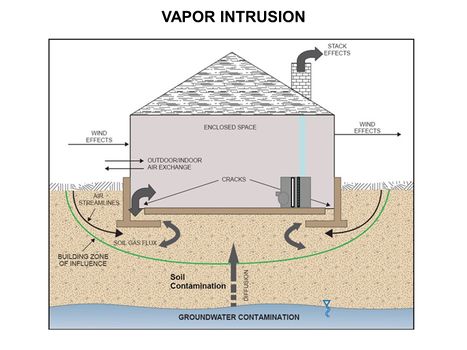
| + | [[File:WH Picture16.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Vapor_Intrusion_(VI)|Key elements of vapor intrusion pathways]] | ||
| + | [[File:WH Picture17.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Sorption_of_Organic_Contaminants|Batch reactor experiments to generate points on a sorption isotherm]] | ||
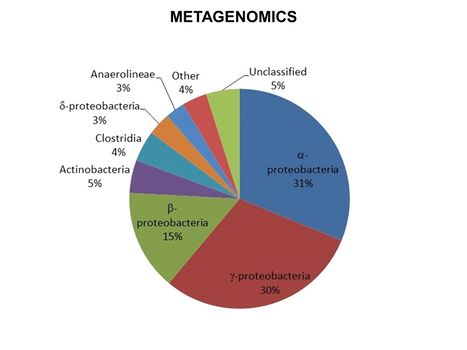
| + | [[File:WH Picture18.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Metagenomics|Results for metagenomic analysis of a groundwater sample obtained from a site impacted with petroleum hydrocarbons]] | ||
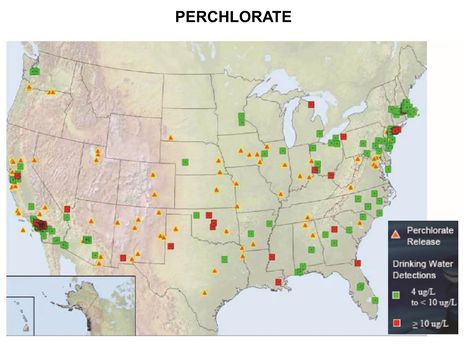
| + | [[File:WH Picture19.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Perchlorate|Perchlorate releases and drinking water detections]] | ||
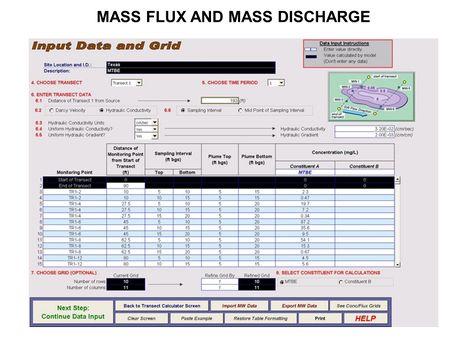
| + | [[File:WH Picture20.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Mass_Flux_and_Mass_Discharge|Data input screen for ESTCP Mass Flux Toolkit]] | ||
| + | [[File:WH Picture21.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Bioremediation_-_Anaerobic_Design_Considerations|Amendment addition for biobarrier]] | ||
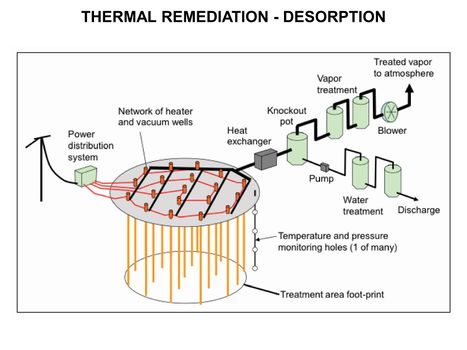
| + | [[File:WH Picture22.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Thermal Conduction Heating (TCH)|Thermal Remediation - Desorption schematic]] | ||
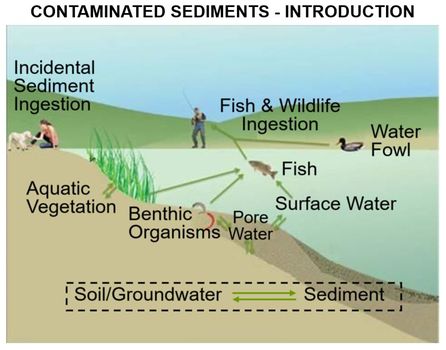
| + | [[File:WH_Picture23.jpg|thumb|center|x350px|link=Contaminated_Sediments_-_Introduction |Key exposure pathways for human health risk from contaminated sediments]] | ||
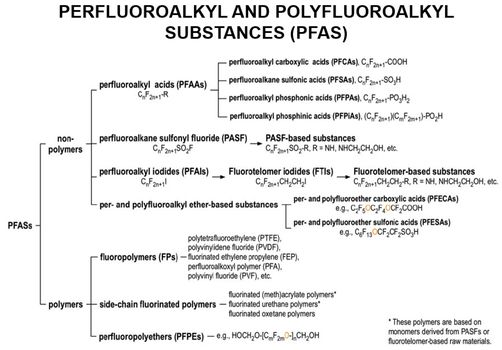
| + | [[File:WH_Picture24.jpg|thumb|center|x350px|link=Perfluoroalkyl_and_Polyfluoroalkyl_Substances_(PFAS)| The PFAS family of compounds]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | </slideshow> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | < | + | {| id="mp-upper" style="width: 95%; margin:3px 0 0 0; " |
| + | | class="MainPageBG" style="width:50%; background:#f5faff; vertical-align:top; color:#000;" | | ||
| + | {| id="mp-left" style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; background:#f9f9f9;" | ||
| + | | style="padding:2px;" |<h2 id="mp-tfa-h2_2" style="margin:3px; background:#cef2e0; font-family:inherit; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; text-align:center; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"><span id="#Table of Contents"></span>Table of Contents <span style="font-size:85%; font-weight:bold;"></span></h2> | ||
| + | {| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top;" | ||
| + | | style="vertical-align:top;" | | ||
| + | <u>'''[[Transport & Attenuation Processes | Attenuation & Transport Processes]]'''</u> | ||
| − | + | *[[Biodegradation - 1,4-Dioxane]] | |
| − | + | *[[Biodegradation - Cometabolic]] | |
| − | + | *[[Biodegradation - Hydrocarbons]] | |
| − | + | *[[Biodegradation - Reductive Processes]] | |
| − | + | *[[Groundwater Flow and Solute Transport]] | |
| − | + | *[[Matrix Diffusion]] | |
| − | + | *[[Metals and Metalloids - Mobility in Groundwater | Mobility of Metals and Metalloids]] | |
| − | + | *[[pH Buffering in Aquifers]] | |
| − | + | *[[Sorption of Organic Contaminants]] | |
| − | + | *[[Vapor Intrusion (VI)]] | |
| − | + | **[[Vapor Intrusion - Separation Distances from Petroleum Sources]] | |
| − | + | **[[Vapor Intrusion – Sewers and Utility Tunnels as Preferential Pathways|Vapor Intrusion - Sewers and Utility Tunnels as Preferential Pathways]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <u>'''[[Characterization, Assessment & Monitoring]]'''</u> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *[[Characterization Methods – Hydraulic Conductivity]] | |
| − | + | *[[Compound Specific Isotope Analysis (CSIA)|Compound Specific Isotope Analysis (CSIA)]] | |
| − | + | *[[Direct Push (DP) Technology]] | |
| − | + | **[[Direct Push Logging | Direct Push Logging]] | |
| − | + | **[[Direct Push Sampling | Direct Push Sampling]] | |
| − | + | *[[Geophysical Methods | Geophysical Methods]] | |
| − | + | **[[Geophysical Methods - Case Studies | Case Studies]] | |
| − | + | *[[Groundwater Sampling - No-Purge/Passive]] | |
| − | + | *[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)|Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)]] | |
| − | + | **[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) - Data Analysis | LTM Data Analysis]] | |
| − | + | **[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) - Data Variability | LTM Data Variability]] | |
| − | + | *[[Molecular Biological Tools - MBTs | Molecular Biological Tools (MBTs)]] | |
| − | + | **[[Metagenomics]] | |
| − | + | **[[Proteomics and Proteogenomics]] | |
| − | + | **[[Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)]] | |
| − | + | **[[Stable Isotope Probing (SIP)]] | |
| − | + | *[[Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume - Bemidji Crude Oil Spill | Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume -<br /> Bemidji Crude Oil Spill]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <u>'''[[Climate Change Primer | Climate Change]]'''</u> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *[[Climate Change Effects on Wildlife]] | |
| − | + | *[[Downscaled High Resolution Datasets for Climate Change Projections]] | |
| − | + | *[[Infrastructure Resilience]] | |
| − | + | *[[Predicting Species Responses to Climate Change with Population Models]] | |
| − | + | *[[Restoration of Ecological Function in Terrestrial Systems Impacted by Invasive Species]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <u>'''[[Coastal and Estuarine Ecology]]'''</u> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *[[Phytoplankton (Algae) Blooms]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | | style="width:33%; vertical-align:top; " | | |
| − | + | <u>'''[[Contaminated Sediments - Introduction | Contaminated Sediments]]'''</u> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | </ | ||
| − | + | *[[Contaminated Sediment Risk Assessment]] | |
| − | + | *[[In Situ Treatment of Contaminated Sediments with Activated Carbon]] | |
| − | + | *[[Mercury in Sediments]] | |
| − | + | *[[Passive Sampling of Sediments]] | |
| − | + | *[[Sediment Capping]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | <u>'''[[Light Non-Aqueous Phase Liquids (LNAPLs)]]'''</u> | ||
| − | + | *[[LNAPL Conceptual Site Models]] | |
| − | + | *[[LNAPL Remediation Technologies]] | |
| − | + | *[[NAPL Mobility]] | |
| − | + | <u>'''[[Munitions Constituents]]'''</u> | |
| − | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Abiotic Reduction| Abiotic Reduction]] | |
| − | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Alkaline Degradation| Alkaline Degradation]] | |
| − | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Composting| Composting]] | |
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Deposition | Deposition]] | ||
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Dissolution | Dissolution]] | ||
| + | *[[Metal(loid)s - Small Arms Ranges]] | ||
| + | *[[Passive Sampling of Munitions Constituents| Passive Sampling]] | ||
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents – Photolysis | Photolysis]] | ||
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Soil Sampling | Soil Sampling]] | ||
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Sorption | Sorption]] | ||
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents - IM Toxicology | Toxicology]] | ||
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents- TREECS™ Fate and Risk Modeling|TREECS™]] | ||
| − | < | + | <u>'''[[Monitored Natural Attenuation (MNA)]]'''</u> |
| − | |||
| − | < | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | *[[Monitored Natural Attenuation (MNA) of Chlorinated Solvents| MNA of Chlorinated Solvents]] | |
| + | *[[Monitored Natural Attenuation (MNA) of Fuels| MNA of Fuels]] | ||
| + | *[[Monitored Natural Attenuation (MNA) of Metal and Metalloids| MNA of Metals and Metalloids]] | ||
| + | *[[Natural Source Zone Depletion (NSZD)]] | ||
| + | *[[Monitored Natural Attenuation - Transitioning from Active Remedies| Transitioning from Active Remedies]] | ||
| − | + | <u>'''[[Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)]]'''</u> | |
| − | |||
| − | </ | ||
| − | + | *[[PFAS Ex Situ Water Treatment]] | |
| − | + | *[[PFAS Soil Remediation Technologies]] | |
| − | + | *[[PFAS Sources]] | |
| − | + | *[[PFAS Transport and Fate]] | |
| + | *[[PFAS Treatment by Electrical Discharge Plasma]] | ||
| − | + | <u>'''[[Regulatory Issues and Site Management]]'''</u> | |
| − | + | *[[Alternative Endpoints]] | |
| + | *[[Mass Flux and Mass Discharge]] | ||
| + | *[[Plume Response Modeling]] | ||
| + | *[[REMChlor - MD | REMChlor-MD]] | ||
| + | *[[Source Zone Modeling]] | ||
| + | *[[Sustainable Remediation]] | ||
| − | + | | style="width:33%; vertical-align:top; " |<u>'''[[Remediation Technologies]]'''</u> | |
| − | + | *[[Amendment Distribution in Low Conductivity Materials]] | |
| − | + | *[[Bioremediation - Anaerobic|Anaerobic Bioremediation]] | |
| − | |- | + | **[[Bioremediation - Anaerobic Design Considerations | Design Considerations]] |
| − | | | + | **[[Design Tool - Base Addition for ERD]] |
| + | **[[Emulsified Vegetable Oil (EVO) for Anaerobic Bioremediation]] | ||
| + | **[[Low pH Inhibition of Reductive Dechlorination]] | ||
| + | **[[Bioremediation - Anaerobic Secondary Water Quality Impacts | Secondary Water Quality Impacts]] | ||
| + | *[[Chemical Oxidation (In Situ - ISCO) | In Situ Chemical Oxidation (ISCO)]] | ||
| + | **[[Chemical Oxidation Design Considerations(In Situ - ISCO) | Design Considerations]] | ||
| + | **[[Chemical Oxidation Oxidant Selection (In Situ - ISCO) | Oxidant Selection]] | ||
| + | *[[Chemical Reduction (In Situ - ISCR) | In Situ Chemical Reduction (ISCR)]] | ||
| + | **[[Zerovalent Iron (ZVI) (Chemical Reduction - ISCR) | Zero-Valent Iron (ZVI)]] | ||
| + | **[[Zerovalent Iron Permeable Reactive Barriers]] | ||
| + | *[[In Situ Groundwater Treatment with Activated Carbon]] | ||
| + | *[[Injection Techniques for Liquid Amendments]] | ||
| + | *[[Injection Techniques - Viscosity Modification]] | ||
| + | *[[Landfarming]] | ||
| + | *[[Metal and Metalloids - Remediation | Remediation of Metals and Metalloids]] | ||
| + | *[[Remediation Performance Assessment at Chlorinated Solvent Sites]] | ||
| + | *[[Soil Vapor Extraction (SVE)]] | ||
| + | *[[Stream Restoration]] | ||
| + | *[[Subgrade Biogeochemical Reactor (SBGR)]] | ||
| + | *[[Supercritical Water Oxidation (SCWO)]] | ||
| + | *[[Thermal Remediation]] | ||
| + | **[[Thermal Remediation - Combined Remedies | Combined Remedies]] | ||
| + | **[[Thermal Remediation - Electrical Resistance Heating | Electrical Resistance Heating (ERH)]] | ||
| + | **[[Thermal Remediation - Smoldering | Smoldering]] | ||
| + | **[[Thermal Remediation - Steam | Steam Enhanced Extraction (SEE)]] | ||
| + | **[[Thermal Conduction Heating (TCH)]] | ||
| + | <u>'''[[Soil & Groundwater Contaminants]]'''</u> | ||
| − | [ | + | *[[1,2,3-Trichloropropane]] |
| + | *[[1,4-Dioxane]] | ||
| + | *[[Chlorinated Solvents]] | ||
| + | *[[Metal and Metalloid Contaminants|Metals and Metalloids]] | ||
| + | *[[N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA)]] | ||
| + | *[[Perchlorate|Perchlorate]] | ||
| + | *[[Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PHCs)]] | ||
| + | *[[Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs)]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 19:25, 30 December 2023
Peer Reviewed. Accessible. Written By Experts |
Your Environmental Information Gateway |
| The goal of ENVIRO Wiki is to make scientific and engineering research results more accessible to environmental professionals, facilitating the permitting, design and implementation of environmental projects. Articles are written and edited by invited experts (see Contributors) to summarize current knowledge for the target audience on an array of topics, with cross-linked references to reports and technical literature. | See Table of Contents |
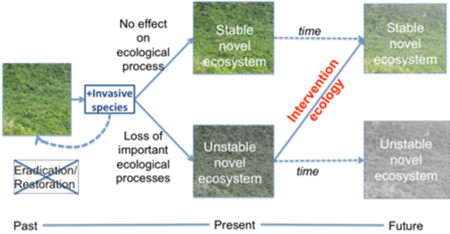
Featured article: Restoration of Ecological Function in Terrestrial Systems Impacted by Invasive SpeciesPer and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) contained in Class B aqueous film-forming foams (AFFFs) are known to accumulate on wetted surfaces of many fire suppression systems after decades of exposure.
Fire suppression systems with potential PFAS impacts include fire fighting vehicles that carried AFFF and fixed suppression systems in buildings containing large amounts of flammable materials such as aircraft hangars. PFAS residue on the wetted surfaces of existing infrastructure can rebound into replacement PFAS-free firefighting formulations if not removed during the transition process. Simple surface rinsing with water and low-pressure washing has been proven to be inefficient for removal of surface bound PFAS from piping and tanks that contained fluorinated AFFF.In addition to proper methods for system cleaning to remove residual PFAS, transition to PFAS-free foam may also include consideration of compliance with state and federal regulations, selection of the replacement PFAS-free firefighting formulation, a cost benefit analysis for replacement of the system components versus cleaning, and clean out verification testing. Foam transition should be completed in a manner which minimizes the volume of waste generated as well as preventing any PFAS release into the environment. Companies are developing new methods to remove self-assembled PFAS bilayers from existing fire-fighting infrastructure so that it can be successfully transitioned to PFAS-free formulations. PFAS sampling techniques used to support firefighting formulation transition activities are consistent with conventional sampling techniques used in the environmental industry, but special consideration is made regarding high concentration PFAS materials, elevated detection levels, cross-contamination potential, precursor content, and matrix interferences. The analytical method selected should be appropriate for the regulatory requirements in the site area. (Full article...) |
Enviro Wiki Highlights |